What is a Cost Sheet?
A cost sheet (cost statement) gives detailed elementwise cost information of a cost object for a certain volume and particular period, ranging from purchasing raw materials to selling goods.
The cost sheet provides a detailed bifurcation of the cost incurred by the entity.
The manufacturing entities prepare these sheets to record the total production cost across various departments. However, the preparation of cost sheets is not restricted to them.
A small business intending to analyze its costs and profit margin can indulge in preparing a cost sheet.
A cost sheet is a formal document that helps in price discovery. A cost sheet contains various cost details relating to the production cost, allowing businesses to determine a selling price.
The cost sheet is usually linked to manufacturing-related businesses. A cost sheet is an important tool in cost accounting that helps in managerial decision-making related to cost controls, comparisons, resource allocation, cost recovery, and optimization of production processes.
Like all accounting reports and statements, the cost sheet is prepared for a specified period.
From total costs to per unit cost, a cost sheet depicts all the components of the cost that went into manufacturing a particular product.
Types of Cost Sheets

Historical cost sheet:
The historical cost sheet considers the actual expenses incurred (direct expenses and indirect expenses). Since this method is based on the actual cost incurred in the past, it is called a historical cost sheet. It is the most commonly used type of cost sheet in various manufacturing businesses.
Estimated cost sheet:
The estimated cost sheet includes the selling price, and future profits are determined by estimating the production costs of a product.
Estimated cost sheets are widely used in service industries and construction businesses, where contract revenue is determined based on the projected costs incurred.
Estimated cost sheets can also be prepared before the start of a business based on accurate and correct data collected by the concerned department.
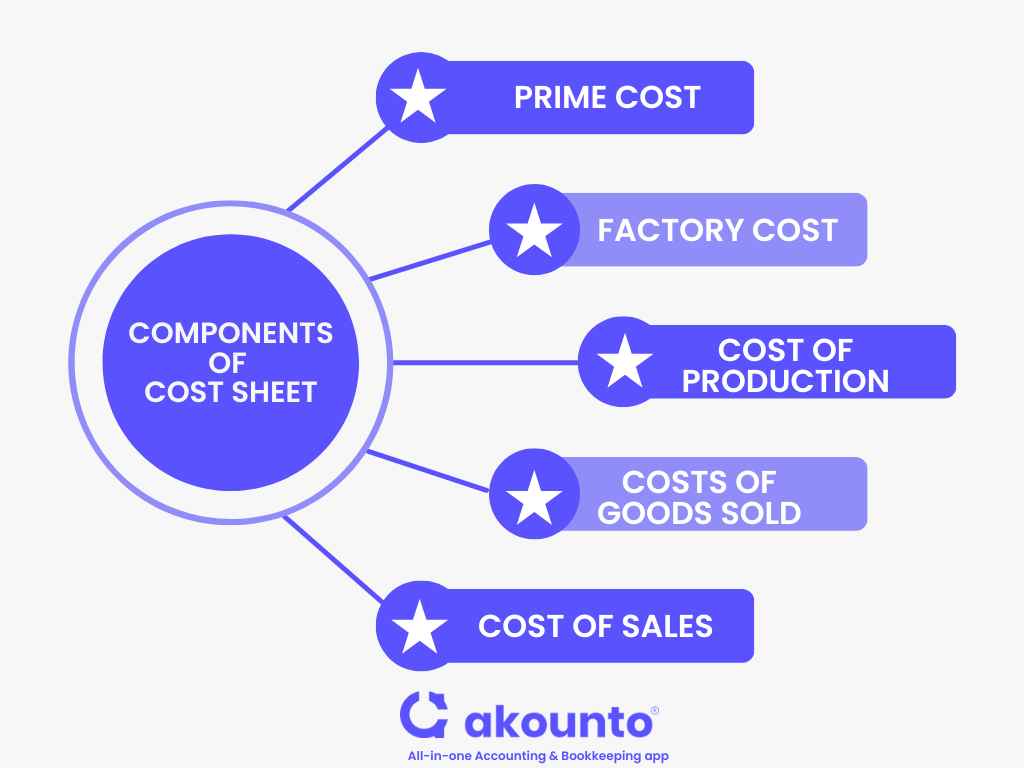
Elements and Components of a Cost Sheet
Components of Cost Sheet
Following are the functional classification of costs that are involved in preparing the cost sheet. They are as follows:
- Direct Material Cost
- Direct Employee Cost
- Direct Expenses
- Manufacturing Overheads
- Administration Overheads
- Selling Overheads
- Distribution Overheads
Cost Sheet: Cost Heads
On cost sheet the functional classifications are grouped in to the following heads:
- Prime Cost
- Factory Cost
- Cost of Production
- Costs of Goods Sold
- Cost of Sales
Each component has a few sub-components incurred gradually as the production progresses. Now let us briefly introduce each sub-component and understand how a cost sheet is prepared.
1. Prime Cost
Prime cost comprises raw materials, labor, and expenses directly attributable to the production process of the entity. The total cost for each element has to be calculated separately.
Prime Cost = Direct raw materials + Direct labor + Direct costs
Direct material cost = cost of material consumed, and this is calculated as follows:
a. Direct material cost = cost of material consumed, and this is computed as follows:
| Opening stock of raw material | XXX | |
| Add: | Purchases * | XXX |
| Less: | Closing stock of raw material | (XXX) |
| Cost of material consumed | XXX |
*Purchases include the cost of the material, freight inwards, insurance, and other expenditure directly attributable to procurement, trade discounts or rebates (to be deducted), etc.
b. Direct labor cost = Total payment made to the employees engaged in the production
It includes:
- Wages and salary
- Incentives and allowances paid to the labor
- Overtime payment
- Bonus & ex-gratia
- Medical benefits
- Retirement benefits etc.
c. Direct cost = any other direct cost
It includes:
- Fuel cost and cost of other utilities
- Rental charges for specific equipment
- Royalty for some particular service
- Fee for technical assistance and know-how
- Amortization of molds, patterns, fixtures, etc.,
- Cost of product/ specific software
- Other costs related to the production of goods or provision of services.
2. Factory cost = Prime Cost + Factory Overheads
Factory overheads are the aggregate of various indirect expenses not directly attributable to the production of goods. Such indirect expenses include:
- Depreciation of machinery
- Payment to employees (Indirect)
- Insurance of plant & machinery, building, factory, etc.
- Other department-related costs
- Repairs & maintenance of factory building, plant & machinery
- Consumables stores and spares
- Lease cost of production assets
In addition to the above, the adjustment concerning the opening and closing stock of the semi-finished goods ( also called work in process) Therefore, the factory cost can be derived as follows:
Factory cost or works cost = Prime cost + Factory overheads + Opening stock of work in progress – closing stock of finished goods
Insight: Work in progress refers to partially finished goods awaiting completion. In other words, Work in progress refers to the raw materials that are undergoing transformation. Hence, they are adjusted to the factory cost to arrive at the actual cost of production.
3. Cost of Production or Office Cost
The cost of production is computed as an aggregate of prime cost, factory costs, and other administrative expenses relating to production.
| Factory cost | XXX | |
| Add: | Quality control costs | XXX |
| Add: | Research and development costs | XXX |
| Add: | Administrative overheads | XXX |
| Less: | Any credit for recoveries ( scrap or by-products) | XXX |
| Cost of production | XXX |
*Credit for recoveries: The realized or realizable value of scrap or waste is deducted as it reduces the cost of production.
The above costs shall be included only if they are incurred in relation to the production activity.
4. Cost of Goods Sold
The cost of goods sold is the cost of production with the adjustment of opening and closing stock of finished goods.
| Cost of production | XXX | |
| Add: | Opening stock of finished goods | XXX |
| Less: | Closing stock of finished goods | (XXX) |
| Cost of Goods Sold | XXX |
5.Total Cost or Cost of Sales
Cost of sales refers to the total cost incurred to make the product available to the customers. This includes the selling expenses, packing charges, distribution overheads, etc.
a. Administrative overheads: Costs related to the general administration of the entity.
- Salary of administrative employees
- Depreciation and maintenance of the building, furniture of the general management
b. Selling expenses: Cost related to the sale of the product. It includes:
- Salary and wages for employees in the sales department
- Cost of advertisement, market research, etc.
- Website maintenance
- Market research expenses
- Repairs & maintenance in the selling department
c. Packing charges: Charges incurred to make the product marketable
d. Distribution overheads: Cost related to the distribution of the product
- Transportation costs
- Insurance relating to the distribution
- Hire charges & maintenance in relation to the distribution vehicles Cost sheet example & format
- Wages to the employees in the distribution department
Therefore, Cost of sales can be computed as follows:
| Cost of Goods Sold | XXX | |
| Add: | Administrative overheads | XXX |
| Add: | Selling expenses | XXX |
| Add: | Packing expenses | XXX |
| Add: | Distribution overheads | XXX |
| Cost of Sales | XXX |
Cost Sheet Format
Arranging the above explained cost-heads in the format of the cost sheet:
|
COST SHEET FORMAT |
|||
|
S.No. |
Particulars |
Amount |
Amount |
|
1 |
+ Direct Materials |
xxx |
В |
|
2 |
+ Direct Labor |
xxx |
В |
|
3 |
+ Direct Expenses |
xxx |
В |
|
4 |
Prime Cost (1+2+3) |
XXXX |
|
| В | В |
xxx |
В |
|
5 |
+ Factory Overheads |
xxx |
В |
|
6 |
+ Opening Work-in-Progress |
xxx |
В |
|
7 |
– Closing Work-in-Progress |
xxx |
В |
|
8 |
Works Cost or Factory Cost (4+5+6-7) |
XXXX |
|
| В | В | В | В |
|
9 |
+ R&D Cost |
xxx |
В |
|
10 |
+ Quality Control Expenses |
xxx |
В |
|
11 |
+ Administrative Overheads related to the Product |
xxx |
В |
|
12 |
+ Primary Packing Expenses |
xxx |
В |
|
13 |
– Scrap Sold / By-Products Produced/ Recoveries |
xxx |
В |
|
14 |
Cost of Production (8+9+10+11+12-13) |
XXXX |
|
| В | В |
xxx |
В |
|
15 |
+ Opening Stock of finished products |
xxx |
В |
|
16 |
– В Closing Stock of finished products |
xxx |
В |
|
17 |
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) (14+15-16) |
XXXX |
|
| В | В | В | В |
|
18 |
+ Administrative Overheads |
xxx |
В |
|
19 |
+ Selling Overheads |
xxx |
В |
|
20 |
+ Distribution Overheads |
xxx |
В |
|
21 |
Cost of Sales (17+18+19+20) |
В |
XXXX |
Cost Sheet Example
The following is the information extracted from the records of XYZ Ltd. for the period from August 1 to August 31. Prepare a cost sheet and also calculate the profit margin
Cost of raw materials Opening 70,000
Closing 60,000
Cost of work-in-process Opening 13,000
Closing 16,000
Cost of stock of finished goods Opening 1,00,000
Closing 1,20,000
Purchase of raw materials 4,90,000
Wages paid 2,50,000
Factory overheads 1,10,000
Administration overheads 60,000
Selling and distribution overheads 35,000
Sales 11,00,000
Solution:
| Particulars | Amount | |
| Opening stock of raw material | 70,000 | |
| Add: | Purchase of raw materials | 4,90,00 |
| Less: | Closing stock of raw material | (60,000) |
| (A) | Raw material consumed | 5,00,000 |
| Add: | Direct wages | 2,50,000 |
| (B) | Prime cost | 7,50,000 |
| Add: | Factory overheads | 1,10,000 |
| Gross Works cost | 8,60,000 | |
| Add: | Opening work-in-process | 13,000 |
| Less: | Closing work-in-process | (16,000) |
| (C) | Factory cost or works cost | 8,57,000 |
| Add: | Administration overheads | 60,000 |
| Cost of production | 9,17,000 | |
| Add: | Opening stock of finished goods | 1,00,000 |
| Less: | Closing stock of finished goods | 1,20,000 |
| (D) | Cost of Goods sold | 8,97,000 |
| Add: | Selling & distribution overheads | 35,000 |
| Cost of sales | 9,32,000 | |
| (E) | Net profit | 1,68,000 |
| Sales | 11,00,000 | |
| Gross margin ( Gross profit/ Sales * 100) | 15.27% |
Importance and Objectives of Cost Sheets For Small Businesses
Objectives
- The principal objective of preparing a cost sheet is to plan the cost of various products produced in the entity and take corrective actions for cost reduction.
- Cost sheets are vital in building an appropriate cost structure that helps managers make significant decisions and budgeting.
- A cost sheet helps monitor an organization’s cash flows and improve operating efficiency.
Importance
The cost sheet helps determine the ideal selling price of the commodities, thereby aiding in achieving the targeted profit margin.
- A business can measure and assess its performance to achieve the targeted profits and find scope for cost reduction.
- Cost sheets contribute to decision-making by providing information for preparing cost allocation budgets for the succeeding periods.
- Cost sheets facilitate reliable comparison of the product cost within and outside the organization and assess the possibility for improvement.
- Cost sheets assist the managers in purchasing materials, labor costs, and overhead expenses, thereby controlling the cost centers.
- Cost sheets help estimate product costs for placing tenders. These tenders can be placed with government departments, companies in the private sector, or any other prospective customer.
- It helps managers decide whether purchasing or producing a component is beneficial.
Quick Tips
The following cost will not form part of the cost sheet:
- Abnormal costs (employee cost during lockdown)
- Penalty, fines, damages, etc.
- Interest and finance charges
However, if the entity receives any subsidy, grant, or incentive from the government, it shall be reduced from the product cost to which such income pertains.
Conclusion
Cost sheet preparation may differ for small businesses that are not engaged in manufacturing. No prescribed cost sheet template must be mandatorily followed by businesses.
The cost sheet document is a tool to track expenses, which is vital in preparing reliable reports. Since they provide a detailed breakdown of various costs incurred, it becomes easy for the owners or managers to make decisions.
Cost sheets are practical, easy to prepare, and help to achieve the targeted costs and the gross profit margin.
Visit Akounto’s blog for similar information and get knowledge to conduct your business operations in an optimal manner successfully.