Bookkeeping involves recording financial transactions, while accounting analyzes financial data to provide business insights.
Bookkeeping is a routine task and involves daily classifying and recording of financial transactions. Accounting, on the other hand, is more focused on analyzing the data or reports compiled by the bookkeeper and making sense of those reports, tables, or financial information.
People often use these terms interchangeably, but despite common objectives, there are differences in their working, end-users, purpose, and processing of financial data.
Accounting as a profession mandates certification, while for bookkeepers, certification is optional. When it comes to filing documents or reports with the IRS or representing your case, CPAs (Certified Public Accountants) are federally licensed for these purposes.
Bookkeeping Vs. Accounting: Basic Understanding
Bookkeeping’s primary purpose is to accurately record transactions for monitoring cash flow, managing expenses, and complying with regulations. It focuses on the day-to-day financial operations of a business.
Accounting analyzes and interprets the financial data recorded through bookkeeping for tasks like preparing financial statements, analyzing performance, and providing tax advice. It’s focused on long-term financial planning and analysis rather than bookkeeping.
The key difference between them is that bookkeeping is about keeping track of the money coming in and going out of a business. Accounting is about making sense of financial data to help businesses make informed decisions.
To further illustrate bookkeeping vs. accounting, here are the key differences.
| Bookkeeping | Accounting | |
| Purpose | Systematic recording and organization of financial transactions | Analysis and interpretation of financial data to provide insights for businesses |
| Scope | Day-to-day financial operations | Long-term financial planning and analysis |
| Main activities | Recording financial transactions, producing financial statements, monitoring cash flow, managing expenses | Analyzing financial data, preparing financial reports and forecasts, and providing recommendations for business decisions |
| Skill Level | Attention to detail, accuracy, organization, and basic math skills | Analytical skills, critical thinking, advanced math skills, knowledge of accounting principles and regulations, including GAAP, tax laws and regulations, and industry-specific standards. |
| Timing | Bookkeeping is performed daily or weekly to ensure that financial records are up to date. | Accounting is done quarterly or annually to analyze financial performance, prepare financial statements, and file tax returns. |
Examples
Bookkeeping Example 1:
ABC Pvt Ltd. Sold merchandise worth $500 to a customer in cash. Here’s a journal entry for bookkeeping related to this sales transaction.
| Account | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash A/c | 500 | |
| Sales A/c | 500 |
In this example, the bookkeeper records the transaction in the general journal, debiting the cash account for $500, increasing the asset account balance, and crediting the Sales account for $500, increasing the revenue account balance.
The entry shows that the company has made a $500 sale and received payment in cash.
Bookkeeping Example 2:
Considering a double-entry bookkeeping system, let’s look at the following example.
Sam bought a bike for $20,000 and paid via bank transfer. The financial transactions the bookkeeper records in the books will be:
| Account | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Bike A/c | 20000 | |
| To Bank A/c | 20000 |
The above record shows that Sam bought the asset (bike) and a corresponding reduction in the bank account.
What Comes First? Bookkeeping Or Accounting?
Bookkeeping comes first and then comes accounting. Bookkeeping records financial transactions, classifies them, and provides basic inputs to generate financial statements. Bookkeeping helps to maintain ledger accounts, their accuracy, and other reports like bank reconciliation, etc. The accountant uses the inputs from bookkeeping to generate financial statements, file them with the IRS, interpret the reports for management, etc.
In many organizations, a CPA is employed as a full-time in-house employee who also functions as a bookkeeper.
The bookkeeping process involves recording daily transactions, such as sales, purchases, payments, and expense receipts, in a systematic and organized manner. It’s usually done using a double-entry accounting system, which ensures that every transaction is recorded twice as a debit and credit entry in the ledger.
The general ledger is a repository for all financial transactions and provides a clear and accurate overview of a business’s financial activity. Bookkeeping also involves reconciling bank statements and ensuring that all financial records are up-to-date and accurate.
Once the transactions have been recorded in the appropriate journals and the general ledger, the accounting process comes into play.
Accounting involves the preparation of financial documents to provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial health and performance.
Overall, both play important roles in financial reporting. While bookkeeping provides the foundation for accurate financial record-keeping, accounting takes it further by analyzing and interpreting the data to provide insights for decision-making purposes.
Bookkeeping or Accounting: Business Perspective
From a business perspective, having an in-house accountant or hiring a bookkeeping team depends on several factors.
An in-house accountant typically has a broader skillset and is responsible for not only bookkeeping but also other key financial topics like financial analysis, budgeting, and tax filings. It’s beneficial for larger businesses that require a high level of financial expertise and need more personalized attention.
Bookkeeping services can be more affordable for a small business owner than supporting a full-time accountant. The team focuses on maintaining accurate transaction records and may include tasks such as accounts payable and receivable, payroll processing, and bank reconciliations.
One advantage of outsourcing bookkeeping is that it allows businesses to access specialized expertise and technology without the overhead costs of hiring an in-house accountant. It also frees up time for a business owner to focus on core operations.
Ultimately, the decision to choose between bookkeeping and accounting services depends on the specific needs and goals of the business, as well as its budget and available resources.
Differences Between Bookkeepers and Accountants
Bookkeepers and accountants have different roles and responsibilities within an organization.
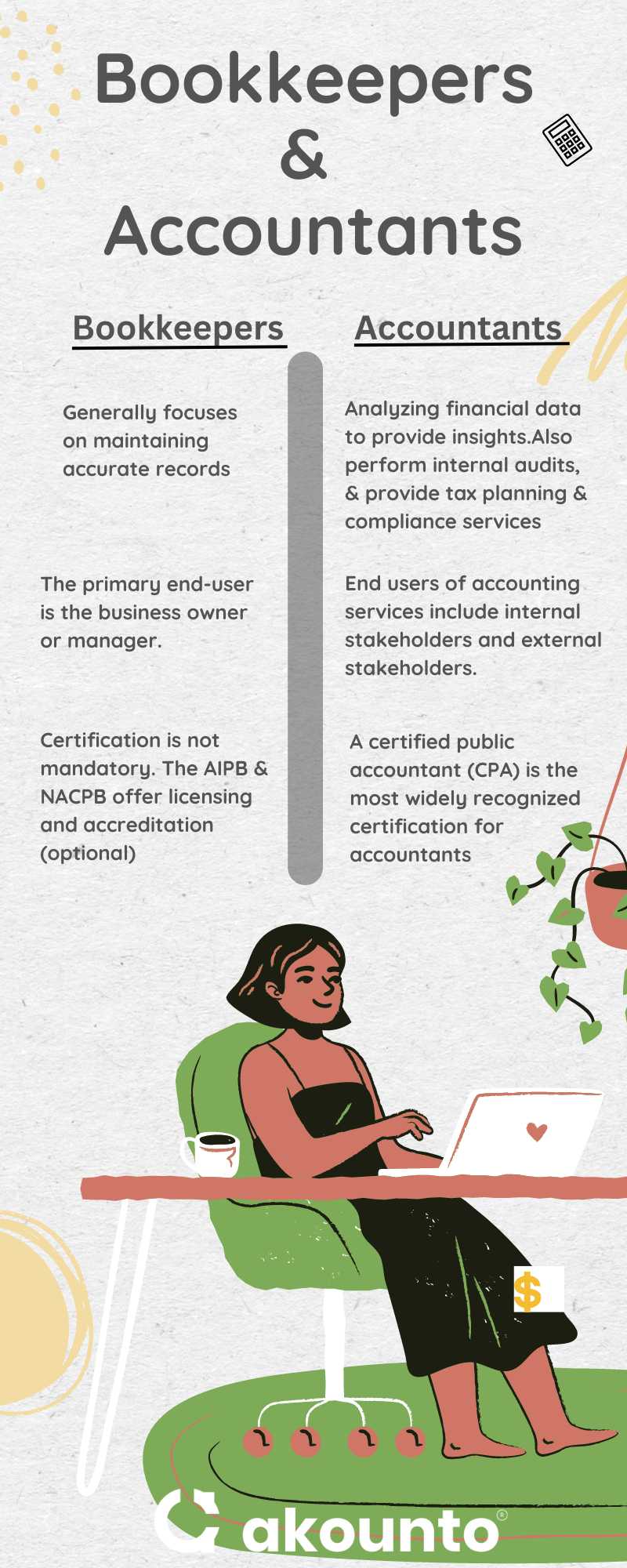
A bookkeeper’s job generally focuses on maintaining accurate records, like recording transactions, reconciling bank statements, and processing payroll. The primary end-user of bookkeeping services is the business owner or manager who needs the financial information to make day-to-day financial decisions.
Accountants’ work is more involved in analyzing financial data to provide insights and make strategic decisions for the business. They may prepare financial statements, perform internal audits, and provide tax planning and compliance services.
The end users of accounting services include internal stakeholders, like management teams, and external stakeholders, such as investors and regulatory bodies.
Skill Sets and Certifications
Regarding skill sets and certifications, a certified public accountant (CPA) is the most widely recognized certification for accountants. Certified public accountants must pass a rigorous exam and meet specific formal education and experience requirements.
Although certification is not mandatory for bookkeeper’s work, their employer or clients may prefer licensed bookkeeping options. The AIPB (American Institute of Professional Bookkeepers) and NACPB (or the National Association of Certified Public Bookkeepers) offer licensing and accreditation to bookkeepers wishing to establish their valuable expertise and credibility in the bookkeeping field.
Accountants and bookkeepers should possess strong analytical and mathematical skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in accounting or bookkeeping software and technology.
Can Bookkeepers Call Themselves Accountants?
Accounting is more complex than bookkeeping and has significant differences from bookkeeping.
Bookkeeping involves recording and organizing financial transactions and does not require certification. Accounting involves interpreting and analyzing the data to provide insights into the financial health of a business.
The accounting profession requires advanced degrees, and accountants should have extensive training and experience in financial analysis. They should be adept with financial principles like the GAAP and be certified by a professional accounting organization.
Bookkeeping is a more routine and administrative task, but accountants may be involved in bookkeeping to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the data.
Similarities Between Bookkeeping and Accounting
Use of Financial Information
Both involve using financial information to track and manage a business’s financial transactions.
Importance of Accuracy And Attention to Detail
Both bookkeeping and accounting require high accuracy and attention to detail to ensure that records are maintained correctly.
Integration of the Bookkeeping and Accounting Process
Bookkeepers and accountants often work together closely to ensure accurate and up-to-date records. They may also collaborate on financial analysis and reporting.
The processes involved in bookkeeping and accounting are often integrated, with bookkeepers providing the data and information that accountants need to prepare financial reports and analyses.
Compliance with Financial Regulations
Both bookkeepers and accountants must comply with financial regulations, such as tax laws and GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles), to ensure that financial reports are accurate and reliable.
Hire an Accountant or Bookkeeper: Factors to Consider
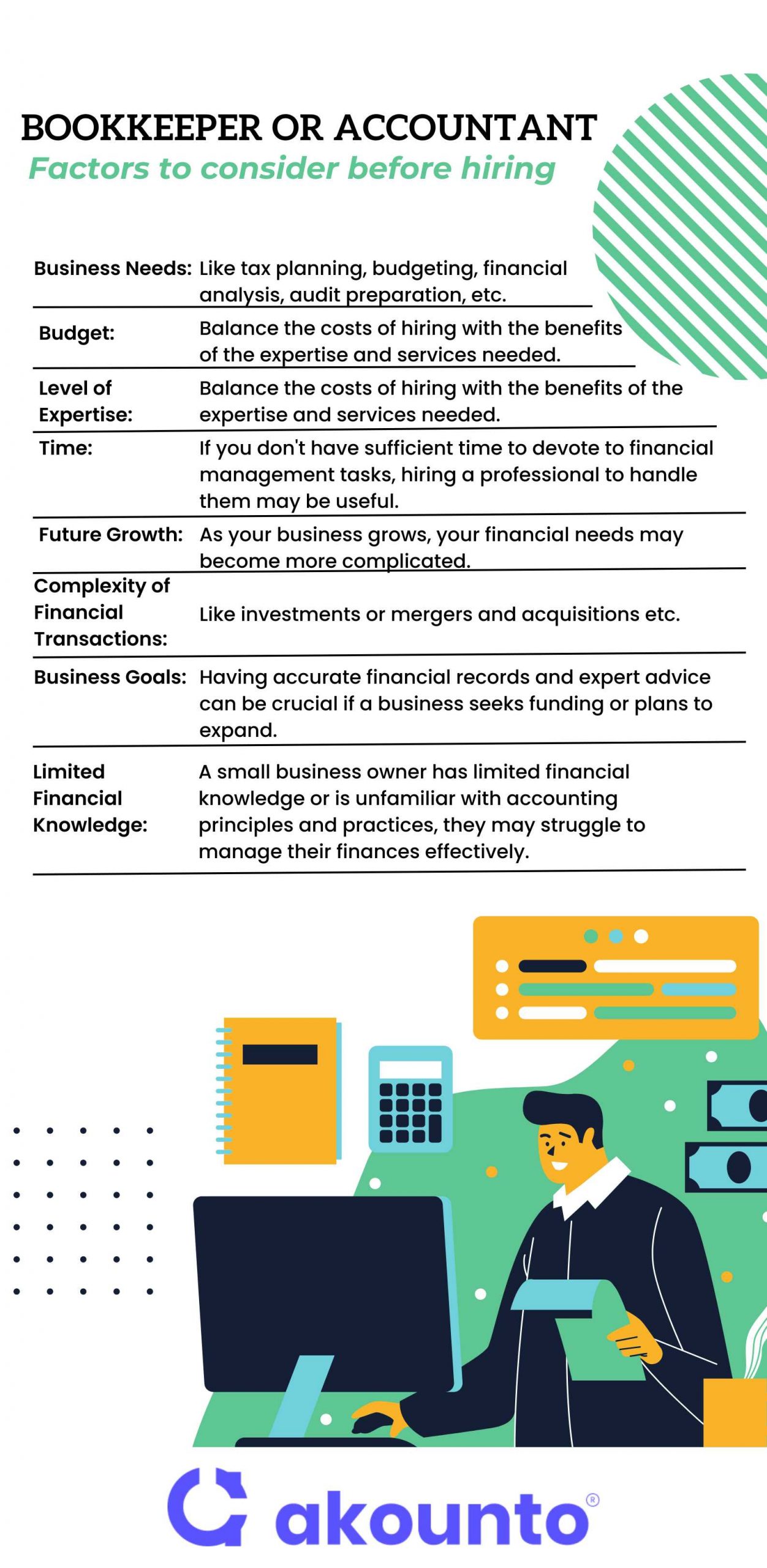
Business Needs
You may want to hire an accounting professional if you need help with tax planning, budgeting, financial analysis, or audit preparation. A bookkeeper may be sufficient if you need help with bookkeeping tasks such as recording transactions, managing business accounts, and reconciling bank statements.
Also, larger businesses with complex financial needs may require the expertise of an accountant, while smaller businesses with simpler needs may be able to get by with a bookkeeper.
Budget
Consider your budget and the costs associated with hiring an accountant or bookkeeper.
Accountants generally charge higher fees than bookkeepers due to their additional training and expertise. You may need to balance the costs of hiring an accountant with the benefits of their expertise and services.
Expertise
Accountants typically have a broader skill set than bookkeepers, with a deeper understanding of financial analysis, tax planning, and other financial management tasks. If you require a high level of financial expertise, you may need to hire an accountant.
Time
Consider the time available to manage your finances. Hiring an accountant or bookkeeper can free up time for you to focus on other aspects of your business. If you don’t have sufficient time to devote to financial management tasks, hiring a professional to handle them may be useful.
Future Growth
As your business grows, your financial needs may become more complicated. It may be beneficial to hire an accountant early on to help you plan for growth and manage your finances more effectively.
The Complexity of Financial Transactions
If your business has complex financial transactions, such as investments or mergers and acquisitions, you may require the expertise of an accountant to handle and analyze these transactions properly.
Business Goals
The financial goals of a business may also influence the decision to hire an accountant or bookkeeper. For example, having accurate financial records and expert advice can be crucial if a business seeks funding or plans to expand.
Limited Financial Knowledge
If a large or small business owner has limited financial knowledge or is unfamiliar with accounting principles and practices, they may struggle to manage their finances effectively. Hiring a professional can ensure the company’s finances are managed correctly and efficiently.
Conclusion
Accurate bookkeeping and up-to-date records allow businesses to provide reliable financials to accountants and stakeholders. They can gain an understanding of a business’s financial health and identify areas for growth and improvement. So, regarding the bookkeeping vs accounting debate, both play critical roles in ensuring a business’s financial success.