What is an Invoice?
Invoices are documents that itemize transactions between two parties for the products or services rendered.
The purpose of an invoice is to maintain a record of the transaction between the customer and the supplier, detailing the goods or services provided, including the price, invoice number, due date, names of the seller and the buyer, taxes, shipping charges, and any other relevant information.
Invoices are considered important financial documents for a business, as:
- They serve as a transaction record that can be used in legal disputes such as fraudulent lawsuits and to protect the parties’ rights.
- They help businesses manage their inventory. An invoice records complete details of the quantity and type of product bought or sold, which can be used to manage the stock levels.
- The financial information on the invoices can be used for financial reporting and tax filing.
- Invoices help build trust and professionalism between buyers and suppliers, protecting a business’s image.
Elements of an Invoice
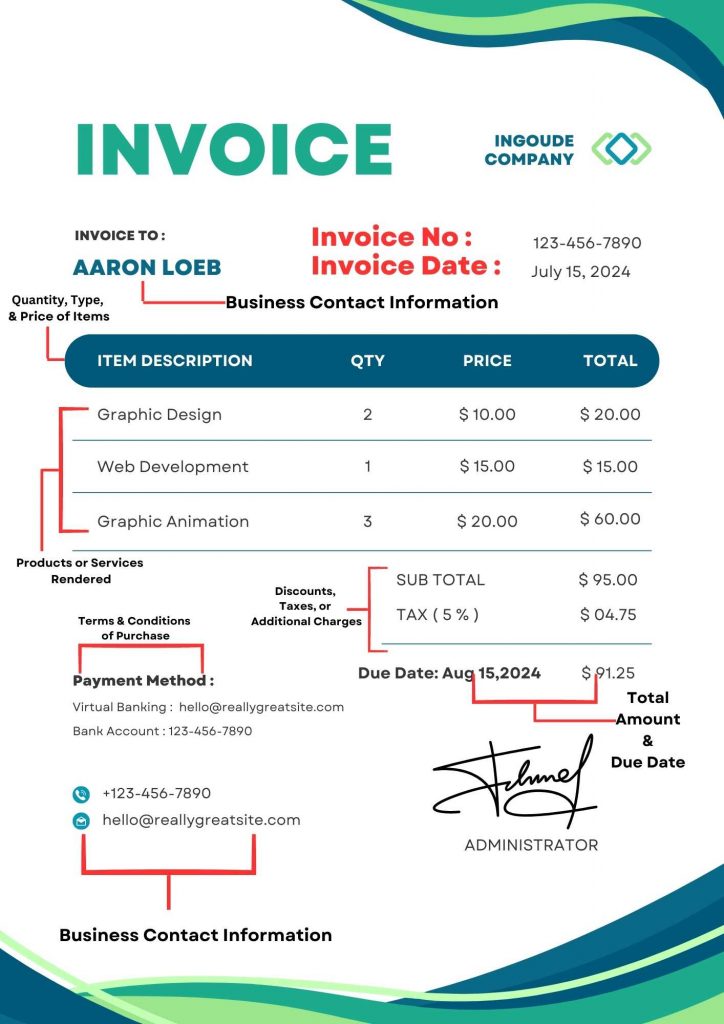
Standard invoice templates invariably consist of the following components:
Invoice Number
Each invoice must have a unique identification number that distinguishes it from others.
Most online invoicing software will assign invoice numbers sequentially, producing a unique identification code for each invoice. Businesses can choose the pattern or format as per convenience, based on the client or period.
Invoice Date
The date at which the invoice was generated is an important component, as it helps keep track of the due date of payment. Invoice date also makes the financial reporting transparent and more efficient for the buying and selling parties.
Business Contact Information
An invoice must feature the complete name of the company, along with its email, contact number, and physical address. Business contact information adds transparency to the invoice and creates a reliable, trustable impact on the customer.
Customer Information
The business invoice should contain the title and full name of the customer, along with the contact number, website, email, and physical address. The exact details will depend upon the customer, whether an individual or another company.
List of Products or Services Rendered
An itemized list of the services rendered or products sold for which the customer owes the stated payment is an important component of an invoice.
Quantity, Type, and Price of Each Item
Against each invoiced item on the list, there should be the exact quantity and price. For instance, the number of a single type of product should be multiplied by the unit price. Similarly, mention the hourly or flat rate for the number of hours for the service provided.
Discounts, Taxes, or Additional Charges
Below the itemized list of products or services provided, mention any discounts and taxes applied or additional charges such as shipping costs.
Total Amount and the Due Date
After applying all the discounts and taxes on the subtotal, mention the date on which the payment is expected, along with the total amount.
Terms and Conditions
The invoice should reserve a space in the footnote for any residual notes, comments, or payment terms. It includes the conditions of the discount application, any surcharges on passing the due date, etc.
Different Types of Invoices
Invoices vary depending on the payment request’s timing and the transaction’s length. Invoices can be classified into four main groups:
- One-time payment invoice
- Project Invoices
- Invoices as Memo
- Other Invoices
Below is the list of the most commons invoices that are a part of these groups:
1. One-time payment invoice
Pro forma Invoice
A pro forma invoice is sent to the buyer or customer as a preliminary bill, which outlines the details of a potential sales transaction. Pro forma invoices do not have legal importance, nor do they represent a complete sale.
Example: Zelda Furniture, a furniture manufacturing company, gets a request for 500 coffee tables worth $125,000 (the price of each table is $250). The business can prepare a proforma invoice enlisting the cost of tables, price per unit rate, any applicable discounts on the bulk order, the total price, and the estimated delivery date.
Looking at the proforma invoice, the customer can obtain the necessary information about the purchase and negotiate a better price or delivery date with the seller.
Sales Invoice
A sales invoice is a legal document the seller generates to request payment from the buyer. It has all the typical components of an invoice, such as the buyer and seller information, details of the products or services, the due amount and date, and the invoice payment terms.
Example: After Zelda Furniture has finished manufacturing 500 coffee tables, the business needs to collect payment from the buyer before it ships the goods. The company can send a sales invoice containing the money they owe and their bank details so that the buyer can pay.
The invoice serves as a transaction record for the buying and selling parties, which can be valuable for accounting and tax purposes.
Consolidated Invoice
A consolidated invoice groups several invoices from the same customer into a single due amount with a single due date.
Example: Zelda Furniture gets another order for 150 coffee tables from the same buyer; after manufacturing the first order, it can send a consolidated invoice that compiles the items of both invoices.
Overdue (or Past Due Invoice)
An overdue invoice remains unpaid beyond its due date. It happens when the buyer fails to complete the payment process within the due date. The seller can take legal action in cases of past due invoices after sending payment reminders.
Example: Zelda Furniture issued an invoice to be paid in 30 days, but the buyer failed to pay even after 34 days. The sales invoice will then become an overdue invoice.
2. Project Invoices
Interim Invoice
Interim invoices are fragmented invoices that contain only a share of the final invoice’s amount and are generally used to help fund the project and cover operational expenses. The interim invoice amount is calculated by the percentage of work completed or the milestones a company achieves throughout the project.
Example: Zelda Furniture agreed to manufacture 500 coffee tables in one year, 250 in the first six months, and another 250 in the later months of the year. After reaching the milestone, the company can generate an interim invoice for $62,500 (for 250 coffee tables).
Timesheet Invoice
A timesheet invoice bills the clients based on the hours spent on the task. Timesheet invoices are common with lawyers, freelance agencies, and consultants.
Example: A client requested a custom coffee table design. Zelda Furniture can provide a timesheet invoice indicating the number of hours spent creating the table and the workers’ hourly rates.
3. Invoices as Memo
Credit Memo (or Credit invoice)
A credit memo is generated when the seller has to provide a refund or a discount to correct a previous invoicing error. Credit memos have a negative total amount.
Example: Zelda Furniture mistakenly charged a customer $100 for a product that costs $80. They could issue a credit invoice for the $20 overcharge. The customer can use the credit to pay for future purchases from the business.
Debit memo (or Debit invoice)
A debit memo is issued when an additional charge exceeds the original amount. Debit invoices help small businesses and freelancers make periodic adjustments to the total amount due according to the project requirements.
Example: Zelda Furniture provided additional services beyond what was originally agreed upon. They could issue a debit invoice for the additional charges.
4. Other invoices
Commercial invoice
A business can issue commercial invoices for its international customers.
Example: Zelda Furniture delivers an order of 100 wooden chairs to a customer from another country. So, Zelda issues a commercial invoice with all the invoice components, complying with the legal requirements. A commercial invoice calculates the tariffs, obtains customs clearance for the shipment of goods within and outside of a country, and determines taxes.
Recurring Invoice
Recurring invoices are issued to customers for services or products provided to them on an ongoing basis.
Example: A customer wants to purchase a monthly subscription for furniture cleaning services. In that case, Zelda Furniture will issue a recurring invoice that will be sent to the customer every month until the subscription is canceled.
All invoices issued for a subscription fee are recurring invoices.
Functions of an Invoice
A legally compliant invoicing process has the following functions:
Tax Filing
Since invoicing keeps the income and expenditures in check, it helps file taxes toward the end of a certain reporting period. Invoicing is a legal requirement in many countries. So, in addition to keeping straight records for taxation, invoices also ensure legal compliance.
Tracking Payments
If a company wants to track transactions with a client, it can simply do so by tracking invoices. With each invoice containing all relevant information, the company never misses late payments, discrepancies in credit duration, or factors affecting the cash flow.
Legal Binding
Invoices can be used as legal proof of agreement in cases of potential fraud and financial misstatements. The business should hence establish payment terms considering each customer’s credit history when it comes to business-to-business dealing.
Business Analytics
Analyzing invoices helps businesses analyze customers’ behavior and buying patterns. The information can significantly help companies boost their sales and marketing strategies.
Record Keeping
The invoicing process acts as an accounting practice since the total amount due becomes the accounts payable for the buyer and the accounts receivable for the seller. In this way, invoice documents help businesses with accurate record-keeping.
Are Invoices Legal Documents?
An invoice keeps a payment record via the specific and unique invoice number but does not have a legally binding status. Invoices leave ample room for manipulation, especially regarding small business invoices.
Invoice vs. Bill vs. Receipt: What’s the Difference?
Invoice vs. Bill
| Invoice | Bill |
| An invoice is usually sent before the payment is made as a request for payment. | A bill is sent after the goods or services have been provided and the payment is due. |
| An invoice offers more detailed information, including the contact details of the parties involved and payment details. | A bill offers limited information only, such as the total amount and applied taxes. |
| An invoice is a comprehensive transaction account between two business parties with a certain due amount and date. | A bill is an amount that is immediately due, such as a restaurant bill, which has to be paid before the customer leaves. |
Invoice vs. Receipt
| Invoice | Receipt | |
| Purpose | An invoice is a request for payment issued by a seller to a buyer. | A receipt is proof of payment given by the seller to the buyer. |
| Timing | An invoice is typically issued before payment is made. | A receipt is generated after the payment has been completed. |
| Content | An invoice contains information such as the details of the goods or services provided, the amount owed, and payment terms. | A receipt typically contains information such as the payment date, amount paid, and payment method. |
| Legal status | An invoice is a legal document that establishes an obligation to pay. | A receipt is not typically considered a legal document. |
| Audience | An invoice is typically sent to the buyer or their accounts payable department. | A receipt is typically given to the buyer as proof of payment. |
| Function | An invoice is used to request payment and keep track of accounts receivable. | A receipt is used to confirm payment and keep track of accounts payable. |
Automate Your Invoicing Process with Akounto
Modern-day cloud-based accounting lets you use electronic invoices instead of physical ones, that is, paper invoices. Electronic invoicing requires minimum inputs and automatically generates various professional invoices on a predefined criterion.
By expediting the process, electronic billing makes it easier to maintain cash flow, ensure timely payments, and offer online payment options for customers.
Akounto is a cloud-based accounting software that can handle all the automated tasks, such as generating digital invoices, keeping track of multiple payments, and helping you build stronger and more efficient client invoicing systems.
Conclusion
An invoice is a fundamental aspect of any transaction. It serves a crucial function in the financial activities of a company, as it is necessary to collect payment for goods or services offered. Automating the payment collection process can enhance efficiency, minimize errors, and save business time and resources.
Tour our Akounto blog section for more information and updates on all accounting subjects.




