Bookkeeping refers to maintaining a record of all financial transactions of the business. It is the practice of organizing and classifying financial records.
What is Bookkeeping?
Bookkeeping is the task of categorizing business transactions as and when they occur. It helps sort all the business’s financial transactions that affect its cash and liquidity status.
Bookkeeping is the responsibility of the bookkeeper of a business firm. The record maintained by the bookkeeper further helps the accountant to analyze the data.
Knowing the bookkeeping basics helps record the increase or decrease in assets and liabilities. The interpreter can also know about the revenue generated or the expenses incurred during business activities.
Methods of Bookkeeping
There are several approaches to bookkeeping. Small business owners can implement the double entry or the single entry system. Cash or accrual-based bookkeeping is also a bookkeeping method followed by businesses.
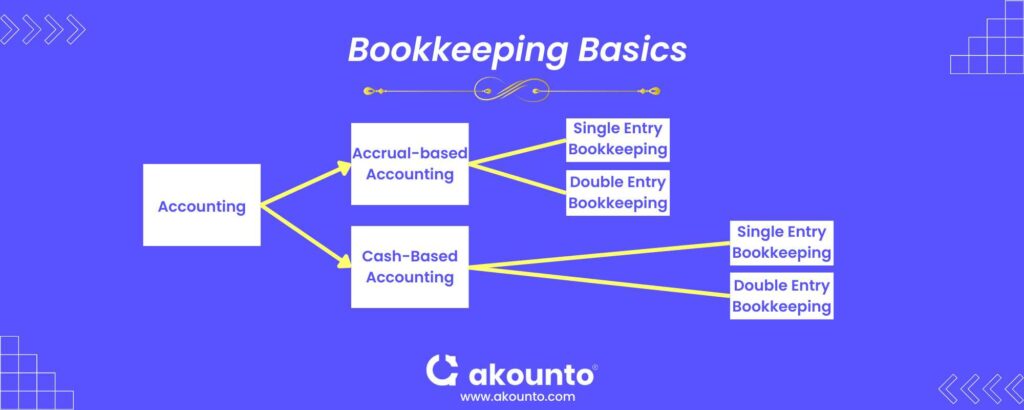
Here is a brief information about these bookkeeping methods.
Single Entry Bookkeeping
A single-entry bookkeeping system helps small business owners record each transaction. The bookkeeper will record only one entry for each transaction in this method.
Most business record financial transactions in the cash book. It helps the bookkeeper record the business’s incoming revenue and outgoing expenditure.
The single-entry bookkeeping system is highly prevalent in small businesses, even if they do not incur any credit transactions.
Double Entry Bookkeeping
The double-entry bookkeeping method follows the principle that every transaction affects at least two accounts.
The basic premise of double-entry accounting is that total credits should always be equivalent to total debits. For instance, if you sell a good worth $100, your cash account will be debited with $100. The sales account will record a credit transaction for the cash receipts of $100.
Every transaction in one account gets followed by a transaction in another account. The double-entry bookkeeping basics are based on the accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
Double entry bookkeeping system is more favorable for large concerns. Big businesses and companies incorporate this bookkeeping system.
Cash-Based Bookkeeping
A business can also choose between a cash-based or accrual-based bookkeeping accounting system. Cash-based bookkeeping will recognize and record revenue or expenditure only when incurred.
Accrual-Based
In accrual-based bookkeeping, the bookkeeper records the transactions when the revenue is earned. The expenses in this bookkeeping method are recorded when they are incurred. The business doesn’t need to see an actual inflow or outflow of cash to record financial transactions in its books.
Bookkeeping For Small Businesses
Small business bookkeeping helps maintain clear records and establishes the basis for separating the business from the owner. The process also supports an accurate representation of the cash flow from business transactions.
With proper small business bookkeeping basics in place, it can always cross-check where it is spending and its sources of revenue. A small business must also maintain its books in compliance with taxation purposes and financial reporting.
Bookkeeping is an essential practice that helps a small business budget to allocate necessary funds for important activities. A business owner can easily review financial accounts to maintain a steady cash flow.
10 Bookkeeping Basics

Every small business owner must maintain ten bookkeeping basics to track overall performance and maintain good financial health.
Assets
The things that help generate revenue for a business are known as assets. Assets are resources with economic value that a business owns. An asset will benefit any business. For example, an accounts receivable account can hike the bank account balances of businesses on their receipt.
Assets are crucial to a business’s or individual’s financial well-being as they generate income. These can be tangible, such as physical objects such as real estate, machinery, vehicles, etc. The intangible assets include non-physical such as patents, copyrights, brands, etc.
Assets also include the following.
- Cash,
- Cash equivalents, such as marketable securities,
- Accounts receivable,
- Inventory,
- Fixed assets, etc.
Maintaining asset accounts helps a business owner learn about its strengths. A bookkeeper maintains all asset account transactions in the general ledger. Bookkeepers may record transactions using bookkeeping software for more precision.
Liabilities
A business can have some debts due, known as liabilities. Liabilities arise when a business is required to repay a loan because of a financial transaction it incurred. It is the money owed by the small business owner to its creditors.
Liabilities represent a claim on a business’s assets. These get settled over time by transferring economic benefits, such as money, goods, or services. Examples of liabilities include loans, mortgages, bonds, credit card debt, accounts payable, and taxes owed.
A business can have long-term and short-term debts. These include
- Accounts payable is the sum a business owes to its creditors or suppliers. A bookkeeper is often responsible for settling accounts payable.
- Loans payable include all the long-term and short-term loans a business gets to keep its operations running. For example, a business can borrow to set up its manufacturing concern.
Equity
Business owners have some ownership in the business. Equity is the share of the business owners or the investors in the business. The business shows information about the equity in the balance sheet.
Equity is also known as shareholder’s equity, stockholders’ equity, or simply equity. It shows all the business owners’ or investors’ claims over the business and represents the residual interest in an entity’s assets after deducting liabilities.
Inventory
Inventory is the number of goods that the business has in stock. These goods have not been sold yet. A business must track and record its inventory to determine future production requirements.
Inventory is a current asset expected to be sold or consumed within one year. It is valued at its cost of acquisition, production, or manufacture. Inventory can take many forms, including raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
A small business owner must maintain an optimal inventory level to meet customer demand. Inventory management is crucial to avoid the costs associated with holding excess inventory. A spreadsheet software can be beneficial in tracking inventory in a better way.
Sales
Sales refer to the revenue generated from selling goods or services to customers. Sales are recorded in the business’s financial records as a credit in the sales account. The corresponding debit is recorded in a revenue/cash account.
Sales are a key metric for evaluating a business’s financial performance. In bookkeeping, sales transactions are recorded using invoices or receipts.
The sales figure can be used to calculate important financial ratios. It helps measure the efficiency of a business using its assets to generate revenue. For instance, a business can easily calculate ratios such as the sales-to-assets ratio.
Purchases
Purchases are the acquisition of goods or services by a business, either for resale or for use in producing other goods. These are recorded in the business’s general ledger as debits in the purchase accounts. The corresponding credit is recorded in an expense account.
Purchases are a key component of a business’s operating expenses. They represent the cost of acquiring the goods and services required to run the business. In bookkeeping, purchase transactions are usually recorded using purchase orders, invoices, or receipts.
Any business can use the number of purchases recorded to calculate important financial ratios. These ratios help measure the efficiency a business uses its purchases to generate revenue.
Expenses
Expenses refer to the costs incurred by the business in the course of doing business. These are recorded in the business’s financial reports as debits in various expense accounts, such as “rent expense” or “salaries expense.” The corresponding credit is recorded in the business’s cash or accounts payable account.
Expenses represent a reduction in the business’s assets. These can be either operating expenses or non-operating expenses. Operating expenses are those that are incurred to conduct the main operations. The non-operations expenses are not directly related to the business’s main operations.
Accurate tracking of expenses is important for small businesses for both tax purposes. It provides information about the business’s spending patterns to determine where costs can be reduced. Tracking them also helps in the management of the business’s finances.
Retained Earnings
Retained earnings in bookkeeping refer to the portion of a company’s net income not distributed as dividends to shareholders. The company instead keeps this portion for reinvestment or other purposes. Retained earnings are recorded in the company’s financial records as an equity component.
Retained earnings accounts represent a company’s net income accumulation over time. The company can use them for various purposes, including reinvesting in the business. A business can arrive at the value of its retained earnings by deducting any dividends declared and paid.
Payroll Expenses
Payroll expenses are the costs associated with paying employees for their work. These expenses are a significant component of a company’s operating expenses. Payroll expenses can be the largest single expense item for many businesses.
In bookkeeping, these expenses are recorded as incurred and included in the company’s financial statements.
Accurate tracking of such expenses in bookkeeping is important for tax purposes and finance management. It provides information about the company’s spending patterns. Their tracking in bookkeeping helps ensure that employees are paid correctly and on time.
Effective management of payroll expenses can help to minimize the impact on cash flow. It ensures the company has sufficient funds to meet its other obligations and determine the payroll taxes.
These days accounting software help in maintaining such bookkeeping accounts.
Income Statement
An income statement is a financial record of operations or a profit and loss statement. It summarizes a business’s bookkeeping record and net income over a specified period.
The income statement typically includes the following sections for record keeping:
- Revenue
- Cost of goods sold (COGS)
- A company’s gross profit
- Operating expenses
- Operating profit
- Non-operating income and expenses
- Net income
An income statement is an important tool for both internal management and external stakeholders. It provides valuable information about the company’s financial performance over time.
Bookkeeping is a crucial aspect of managing a business’s finances, and having a solid understanding of its basics can help you maintain your business bank statements efficiently. With Akounto accounting software, bookkeeping becomes a breeze as the platform offers a range of features that automate financial processes, saving you time and energy.
For more information on accounting, bookkeeping services, and more, visit our website today!




