What is Burden Cost?
The burden cost refers to all indirect costs associated with employing or maintaining employees or inventory beyond direct compensation.
It typically includes payroll taxes, workers’ compensation, health insurance, paid time off, training, travel expenses, vacation, sick leave, pension contributions, and other benefits.
It determines a company’s actual cost to hire and maintain its employees to ensure a smooth manufacturing process.
Types of Burden Cost
There are two types of burden cost – project burden cost and material burden cost.
Project Burden Cost
It is an unavoidable cost that a business must incur when working on a project. The drawback of these costs is that one cannot assign the benefits of burden cost to any other project costs because they are specific to a project. There will be a new set of burden costs for a new project like equipment, salaries, travel, etc.
Material Burden Cost
It involves material expenses that hike the full cost of producing or manufacturing a product. Usually, these costs are hidden, and a business must assess them to understand what is driving up its cost of production.
For example, expenses such as insurance, rent, and utilities are taken care of by the business every month, so these sometimes go unregarded and should also be calculated in the cost of production.
What is Burden Rate?
In order to accurately depict the costs associated with manufacturing or providing a good or service, the burden rate is the allocation of indirect costs to direct costs, such as labor or inventory.
The burden rate is computed by adding burden cost to direct cost in order to present a product’s total observed cost.
The burden rate is the rate at which burden costs are applied to direct costs. It includes extra liabilities related to labor costs. It is frequently referred to as the hidden cost of staff retention.
Types Of Burden Rate
There are two types of burden rates,
- Labor burden rates: The labor burden rates involve the overhead cost related to labor.
- Inventory burden rates: The inventory burden rate usually includes the machine time overheads hidden for a business.
How does Burden Rate Work?
Labor or inventory burden considers extra liabilities or indirect costs a business must bear while operating. These liabilities accrue the benefits a business gives its employees besides the paid time.
Direct costs are directly connected with the production of goods. Such costs are typically variable, such as wages, labor, manufacturing supplies, and material expenses.
Indirect costs are associated with running a business and are not directly accountable to a product. For example, these can include electricity or gas, administrative expenses, advertising costs, etc.
Businesses often calculate burden rates to compare direct and indirect costs and determine the actual project costs of your business. It helps a business know whether taking on high-value projects is worth it.
Benefits of Tracking Burden Rate
Tracking the burden rate offers several advantages to a business, including:
Feasibility of an In-house Manufacturing Plant
A burden rate will help you determine whether it is feasible to establish a manufacturing plant in-house. If the analysis turns out expensive, a company can consider installing the manufacturing plant outside the home country.
Burden rate analysis helps understand if the labor burden rate and manufacturing overhead costs will be high or low in the area of operation.
Saves a Business from Heavy Losses
Conducting a budget rate analysis is crucial as it saves a business from incurring heavy losses. It can help identify and eliminate unnecessary costs. Most companies calculate the burden rate to approximate their spending on inventory and employees.
Data-Driven Decisions
Calculating and tracking the burden rate helps businesses make informed decisions such as expansion, layoffs, new hires, and location changes. It offers a greater understanding of the company’s financial standing and improves strategies to meet the goals.
How to Calculate Burden Cost?
Calculating burden rate or cost involves two business costs – labor burden rate and inventory burden rate.
How To Calculate The Labor Burden Rate?
It includes direct and indirect labor costs a business must pay beyond its regular salaries and wages. The labor cost includes the following.
- Payroll taxes
- Workers Compensation
- Health insurance
- Education
- Travel
- Pension
- Other benefits
All these costs add up to determine the labor burden rate. This cost or burden rate is generally higher for senior employees as they are entitled to other benefits, including fringe benefits.
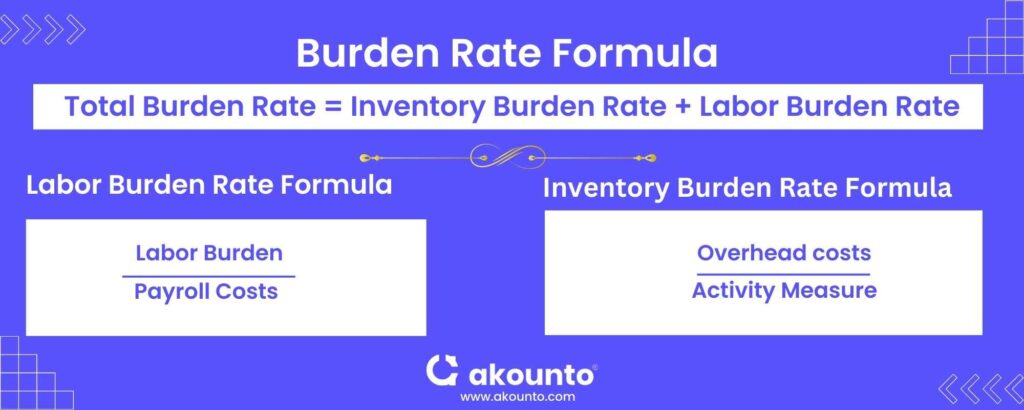
The burden rate formula for determining the labor burden is:
Labor burden/payroll costs = burden rate (for labor)
How to Calculate Inventory Burden Rate?
A business should determine the inventory burden rate to simplify the comparison between a business’s direct and indirect costs.
Businesses must calculate the inventory burden rate separately, considering the machine hour. You must convert the inventory burden into an hourly cost rate to determine this cost.
The inventory burden rate directly impacts the total cost of production.
A business must add the inventory burden cost to the production total to determine the true cost of production.
For calculating the inventory burden rate, the formula is as follows:
Overhead costs/ activity measure = Burden rate (for inventory)
Burden Rate Formula
Burden rate calculation involves two different costs; labor and inventory burden cost. A business must add both costs to arrive at the actual burden rate.
Total burden rate = Inventory burden rate + Labor burden rate
Burden And Overhead Costs
Burden costs have a significant impact on the production total of a company. They hike the overhead costs of a business. However, overhead cost does not necessarily involve burden rates. It can include expenses, such as rent and other factory overhead costs.
Business Decisions Based on the Burden Rate
A business can make better-informed financial decisions by considering the burden rate. Making business decisions based on the burden rate becomes simple with the following tips.
- Cut Indirect Production Costs – A business can save a lot of additional costs if it checks the burden rates regularly.
- Record in Spreadsheet – A business needs to record all past such costs in a spreadsheet. It makes revisiting these costs easier.
- Double-check your numbers – Always ensure that you double-check the numbers when you calculate the labor burden rate to ascertain the burden cost.
Final Words
Managing expenses is crucial for a small business. Burden and overhead costs add to a considerable expenditure which can adversely impact the ROI of a project.
Optimizing business operations and increasing efficiency needs professional management of finances and expert support for informed decision-making. VisitВ AkountoВ and handle your finances like a pro.




