What Is Non-Operating Income?
Non-operating income is part of a company’s revenue from non-core business operations.
Non-operating income is an additional source of revenue for the company and is strategically important because it acts as a safety cushion against losses in the business’s operations.
When an entity’s operating performance is down due to low demand, market competition, business cycles, etc., the non-operating income offsets the deficit in revenues to some extent and ensures the business’s solvency.
A startup, small business or company with an innovative product may struggle initially to generate revenue from core operating activities, then non-operating income helps to augment profitability and sustain the business operations for a long time.
Subtract operating income from the company’s total income to calculate non-operating income.
Examples of Non-Operating Income
Investment Income
Income generated from an investment not directly linked to the core business operations, like investment in land, real estate, intellectual property, cryptocurrency, commodities, art, and collectables, etc.
Income from Non-core Business Operations
Income from rent, patent earning, insurance settlement, royalty etc.
Asset Impairments
Income earned due to a write-down of obsolete assets. Asset impairment also included income from the sale of non-core assets.
Dividend Income
Dividends are received due to investment in stocks and similar financial instruments unrelated to the company’s core operations.
Interest Income
Interest from bonds, treasury bills, debt securities, gilt funds etc. The investments in these funds do not form a part of core business activities.
Currency Fluctuations
Income is generated due to changes in exchange rates when a business is dealing in foreign exchange transactions to settle international trade of goods or services.
Government Grants
Government incentives or grants received for non-core business operations like research and development, environmental initiatives, SEZ development etc.
Litigation Settlement
Income generated from the settlement of legal disputes or awards from arbitration bodies for the cases/issues which do not form part of fundamental business operations.
Non-Operating Income and Income Statement
Non-operating income is commonly referred to as “other income”; it is also known as “income from non-core activities”.
Non-operating income is contextual to the type of business. Most non-operating income is not regular, also called “peripheral income” or “incidental income”.
An entity’s income statement shows income, expenses, and net (profit or loss) over a specific period. Income comprises operating and non-operating income.
EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes) is operating income, including income from the company’s core business operations. It helped to understand the operating efficiency and computes operating profit as a metric.
Non-operating income includes all the non-operating gains and losses arising from activities outside the purview of fundamental business activities. Due to this reason, non-operating income is shown separately in the income statement below the operating income section.
To calculate the company’s EBT (earnings before taxes), non-operating and operating income are added. EBT provides an overview of the company’s financial health and profitability.
There can be non-operating losses or profits depending upon the non-operating expenses being higher than the non-operating income and vice versa.
Investors and stakeholders are keen on separating non-operating income from operating income to ascertain the impact of core business operations, the company’s earnings from fundamental activities, market relevance and potential growth.
SEC Requirements for Non-Operating Income Reporting
S-X 5-03(7) and (9) is a regulation from the SEC that requires public companies to report non-operating income and non-operating expenses separately on their income statements. In the income statement, after the operating profit line item (operating income line), non-operating income is depicted.
S-X 5-03 mandates the companies to report in the income statement or the footnote about the loss or profit on securities and income deductions.
S-X 5-03 regulations state that in the footnote or the reporting entity’s income statement, the amounts earned from the following items should be presented (also disclosed u/s S-X 4-08(k))
- Dividends
- Interest on securities
- Profits in securities
- Other income
Advantages of Non-operating Income

- Neutralize losses: Offsetting losses due to various non-operating expenses like asset impairments.
- Additional funds: Frees up capital for growth and expansion by reducing the impact of interest payments and other interest expenses.
- Diversify income sources: An increase in net non-operating income directly adds to the company’s total income and helps diversify income streams.
- Pay fewer taxes: Sometimes, non-operating income is taxed at a lower rate.
- Forex windfall: For multinational corporates or small businesses dealing in exports, foreign exchange transactions can result in gains due to favourable changes in foreign exchange rates.
- Capital gains: These may result in capital gains from financial securities or other capital asset transactions.
Disadvantages of Non-operating Income
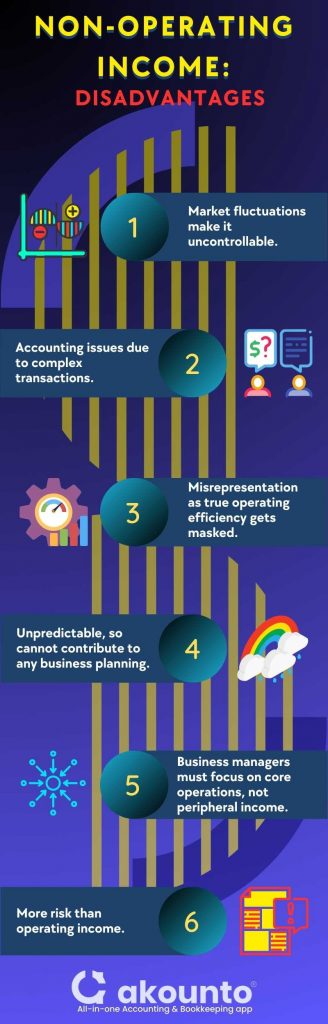
- Market fluctuations: Operating or incidental income depends on external factors that are not in the control of any management teams.
- Accounting issues: Due to complex and untimely transactions, following accounting principles for recording transactions on financial statements becomes challenging.
- Misrepresentation: When non-operating income is used to counterbalance net operating income, the true operating efficiency gets masked.
- Unpredictable: Management teams cannot predict non-operating income. Thus, it cannot contribute to any business plan or estimation of future revenue streams as it is not recurring.
- Distraction: Business managers must focus on core operations, not peripheral income. Any significant impact of peripheral income also disturbs the trends and income forecasts.
- Risk: Non-operating income can involve more risk than operating income, as factors are not in the control of management, and losses can be huge if expectations are not met.
Non-Operating Income vs Operating Income
|
Non-Operating Income |
Operating Income |
|
Income generated from non-core business activities. |
Income generated from primary business operations. |
|
It is incidental, peripheral and not regular. |
It is a recurring, permanent and main source of income. |
|
In the income statement, it is reported as a separate line item below operating income. |
It is the difference between income and (COGS) cost of goods sold minus operating expenses. |
|
It can inflate the total earnings of the company even if the core business operations are not performing up to standards. |
It represents a clearer picture of the financial health of the company in terms of its profitability and efficiency of internal operations. |
|
Examples include:
|
Examples include:
|
Conclusion
Non-operating income be advantages and disadvantages for businesses, from an additional source of revenue to a more volatile and unpredictable income. Tracking income sources is very important than just counting profits.
The composition of income and profits can be well classified and reported using accounting software like Akounto which gives detailed reports for data-driven decision-making.




