An outstanding invoice represents a customer’s financial obligation to the supplier or service provider for products or services availed. It typically includes details of the invoice number, amount owed, payment terms, due date, payment options, and any applicable late payment fee or early payment discounts.
The customer is expected to make payment of the invoice before the payment deadline. But if the customer fails to pay by the invoice due date, it becomes an overdue or outstanding invoice.
All overdue payments and unpaid invoices are considered outstanding invoices regardless of whether they are within the payment terms or have exceeded their due dates until they get paid.
Impact on Cash Flow and Business Operations
Outstanding invoices can significantly impact a business’s cash flows and financial stability in the following ways.
Disruption in Cash Flows
Outstanding invoices directly impact a small business’s cash flow. The outstanding payments and unpaid invoices disrupt the expected cash inflows into the business, limiting its ability to cover operating expenses, meet financial obligations, and make investments for future growth.
Working Capital Constraints
Small businesses often have limited working capital. The outstanding payment ties up a significant portion of the business revenue, leading to fund shortages to invest in equipment, inventory, marketing, compensation of employees, and other business needs on time.
Increased Financial Stress
Small businesses generally rely on timely payments to sustain business operations and meet financial obligations like rent, utilities, loans, etc. A business may be forced to borrow funds or rely on credit lines to compensate for outstanding invoices, resulting in additional interest expenses and debt that will strain its financial stability and profitability.
Difficulty in Planning & Forecasting
Unpredictable cash flow resulting from delayed payments can disrupt forecasting and budgeting efforts, making it difficult to make informed decisions regarding business growth, hiring, and investment, impeding the business’s long-term sustainability and competitiveness.
Strained Supplier Relationships
If the business is unable to pay its suppliers promptly due to outstanding invoices, it can strain relationships and disrupt the supply chain. Suppliers may reduce credit limits, impose stricter payment terms, or even refuse to continue doing business with the company.
Administrative Burden
Businesses may need to allocate additional resources and staff to track outstanding invoices, charge late fees, manage collections, send payment reminders for outstanding and unpaid invoices, and handle disputes, diverting time, attention, and resources from core business activities.
Increased Bad Debt Risks
If invoices remain outstanding for extended periods, there is a higher risk of customers defaulting or the payment becoming uncollectible. It can lead to bad debt write-offs, negatively impacting the business’s financial statements and profitability.
Types & Examples
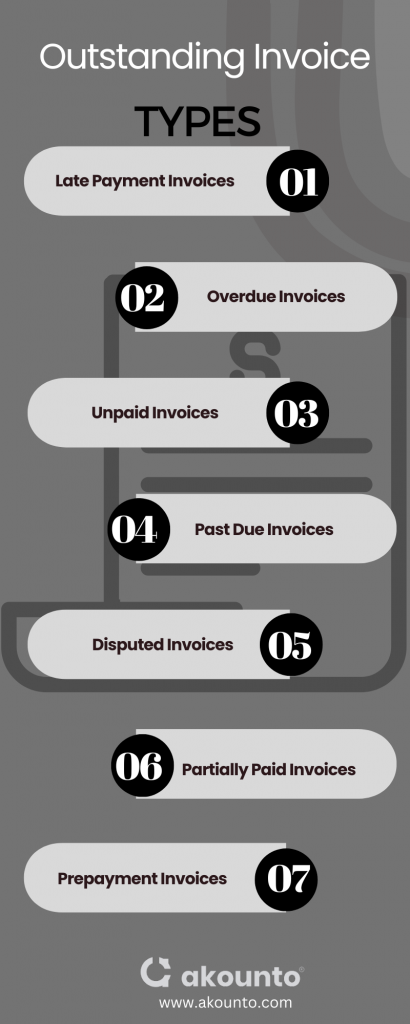
Several types of outstanding invoices can occur in business transactions. Here are some common examples:
- Late Payment Invoices: refers toinvoices customers have not paid within the specified payment terms or due date. The term indicates the payment is overdue but does not necessarily imply a breach of the agreed terms. The invoice is considered an outstanding invoice until the payment is settled.Example: A customer is required to pay an invoice within 45 days. But fails to pay within the stipulated time and pays after the delay of 10 days, i.e., the 55th day. So, it is considered a late invoice as it was not settled within the specified payment deadline.
- Overdue Invoices: refer to invoices that have significantly surpassed their agreed payment due dates without being paid. The late payers may face interest charges, penalties, or strained business relationships due to a breach of the agreement.Example: An invoice has a payment due date of April 15, 2023. But, the customer fails to pay the invoice, and several weeks pass without payment. The invoice will be considered overdue invoice, and the seller can take action against the buyer, per their agreement, to recover the overdue amount.
- Unpaid Invoices: includes outstanding and unpaid invoices that are still within the payment terms but have not been paid and invoices that are past due. The invoices will remain outstanding till they get paid.Example: A supplier provides goods and issues an invoice to be paid by July 16, 2023. The invoice will be considered an unpaid invoice till the customer settles the amount owed, regardless of the payment date.
- Past Due Invoices: are invoices that have exceeded their payment due dates. These invoices are considered outstanding and may incur late fees or interest charges as per the payment terms.Example: An invoice is issued with an invoice due date of September 1, 2023. But the customer fails to pay the invoice even after three months. It will be considered a past-due invoice and may incur charges per the agreed past-due terms.
- Disputed Invoices: arise when there is a disagreement or discrepancy between the customer and the business regarding the amount owed or quality of goods or services provided. The invoice remains outstanding until the dispute is resolved.Example: ABC Corporation issued an invoice of $5,000 for delivered goods. However, the client disputes the quantity and quality of the goods received. The invoice will remain unpaid until the dispute is resolved through negotiation or mediation.
- Partially Paid Invoices: In some cases, customers may make partial payments of an invoice, leaving a remaining balance unpaid. These invoices are considered outstanding until the full amount gets paid.Example: ABC Inc. received an invoice from CSG Corporation. for $3,500 for consulting services. CSG made a partial payment of $2,500, leaving a remaining balance of $1,000. The invoice is considered partially paid until the outstanding balance is settled.
- Prepayment Invoices: Some businesses require customers to make deposits before the goods or services are rendered. If the customers fail to meet the payment requests, their invoices will remain outstanding until they are settled.Example: XYZ Corporation has engaged ABC Company for a website development project. To secure the services, XYZ made a prepayment of $7,000. ABC issued a prepayment invoice on June 1, 2023, to reflect the amount received and state the remaining balance to be invoiced upon project completion.
Outstanding Invoice vs. Past Due Invoice
| Basis | Outstanding Invoice | Past Due Invoice |
| Meaning | It includes invoices that have not been paid in full by the customer. | It refers to invoices that have exceeded their payment due dates. |
| Payment Timeframe | It encompasses all unpaid invoices, regardless of the due date. | It includes invoices that have surpassed their payment due date. |
| Late Fees | Invoices may or may not incur late payment penalties, depending on the agreement. | Past-due invoices may incur a late fee or penalty for exceeding the due date. |
| Collection Efforts | Outstanding invoices require follow-up and collection efforts to secure outstanding payment. | Past-due invoices require additional efforts to collect overdue payments. |
Preventing and Managing Outstanding invoices
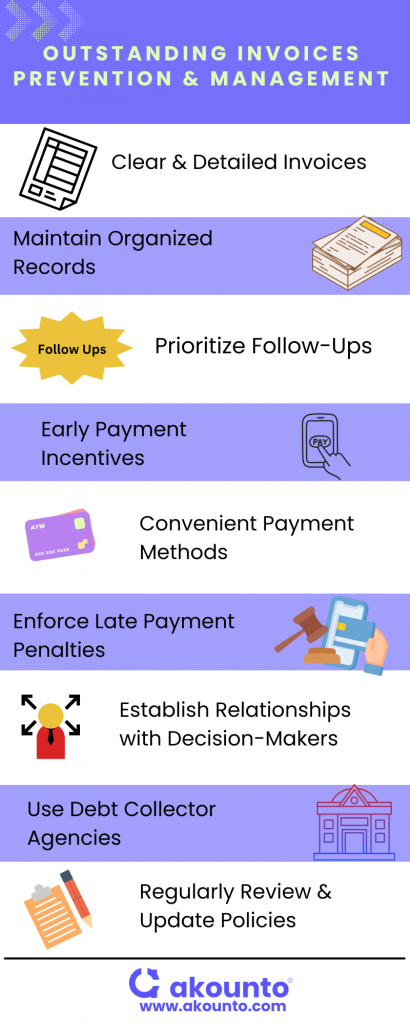
A small business owner can use the following ways to prevent and manage outstanding invoices and maintain healthy cash flow.
Clear and Detailed Invoices
Ensure that the invoices are clear and accurate. They should include relevant details, like unique invoice number, due date, itemized charges, any upfront deposits or partial payments for long-term projects, and the business’s contact details. It helps avoid confusion and gives clear instructions for payment.
Maintain Organized Records
Keep meticulous records of all invoices, customer details, communications, and payment due dates. Consider using automated systems or accounting software to streamline the invoicing process. It can help you classify an outstanding invoice from other types to track an outstanding payment better.
Prioritize Invoicing Follow-Ups
Foster strong relationships with customers through excellent customer service and open communication to establish trust and good rapport that can encourage timely payments and reduce the likelihood of disputes.
Proactively communicate with customers regarding their outstanding invoices. Send them polite and regular invoice reminders via a reminder email, follow-up with phone calls, or statements to keep them informed about the unpaid balance andfurther administrative and legal action the business may take for their late payments.
Early Payment Incentives
Provide incentives such as rewards or discounts to customers who pay early or on time. It encourages prompt payment and creates a positive incentive for customers to settle their invoices.
Convenient Payment Methods
Offer flexible payment options like credit cards, online payments, and direct bank transfers. In certain cases, customers may be experiencing temporary financial difficulties. Consider offering payment plans or negotiating alternative terms to accommodate their situation.
Businesses can establish clear credit policies, perform credit checks, and set appropriate credit limits to ensure they receive payment in a structured manner and allow customers to settle their invoices promptly.
Enforce Penalties for Late Payments
Clearly state late payment penalties in the payment agreement and enforce them consistently. Late payment fees or interest charges can be an additional incentive for customers to pay on time.
Establish Relationships with Decision-Makers
If a small business is dealing with larger organizations, try to establish relationships with the appropriate decision-makers or accounts payable departments. Building rapport can help expedite the payment process and promptly address any payment issues or disputes.
Utilize Debt Collector Agencies or Legal Assistance
If the efforts to collect outstanding invoices are unsuccessful, the business may need to enlist the services of professional debt collectors or seek legal assistance to recover the outstanding debt. Before proceeding with this option, it is important to understand the costs and potential impact on customer relationships.
Regularly Review and Update Policies
Evaluate and update the invoicing and collections policies regularly based on your experiences. Identify any recurring bottlenecks in the payment processes, create a payment strategy, and adjust accordingly to enhance efficiency and effectiveness to get outstanding and overdue invoices paid.
By implementing these measures, a small business can reduce the risk of outstanding invoices, have customers pay outstanding invoices, maintain a healthy cash flow, and build stronger financial foundations.
Conclusion
Effectively managing outstanding invoices and maintaining a healthy cash flow are crucial for the success of small businesses. Building strong client relationships, implementing proactive invoicing and follow-up practices, monitoring accounts receivable and payment trends, and evaluating credit policies can help streamline the invoicing processes and ensure timely payment.
Use Akounto’s invoicing software to create professional invoices, send automatic outstanding invoice reminders, manage accounts receivables, and more to get paid faster.




