What is Tax Accounting?
Tax accounting is processing accounting information to estimate tax assets and liabilities for an individual or a business. Tax accounting is governed by Internal Revenue Code (IRC) and aims to calculate taxable income.
Tax accounting principles and standards are mentioned in Internal Revenue Code (IRC) provided byВ Internal Revenue ServiceВ (IRS). It is not governed by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles(GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), as they provide the accounting standards for general accounting and reporting.
Tax accounting focuses on preparing financial documentation for taxation purposes, including filing tax returns and determining tax obligations at the state and federal levels.
The taxable income derived from tax accounting could differ from that reported in the income statement. The difference is due to the tax code, which has a different method for recognizing income and expenses than GAAP or IFRS.
Tax accountant helps individuals and firms get the exact amount that is to be paid by them to IRS.
Tax Accounting Principles in the United States
IRS has issued some codes that benefit taxpayers and ease their work during tax season. The code helps an organization determine its tax payments and ensures that financial transactions are recorded per the internal revenue service regulations and meet compliance standards.
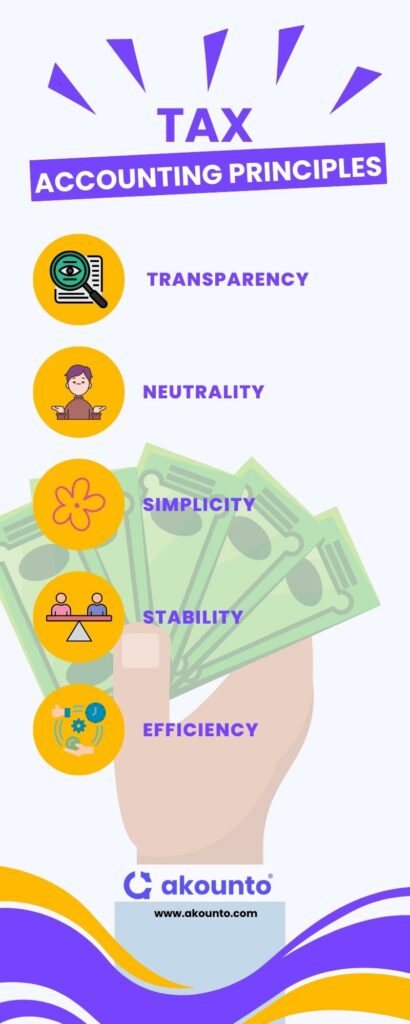
The important tax accounting principles are:
Transparency
It clearly defines the procedure to calculate the taxable amount and total tax. Also, to ensure that financial records are maintained as per law and meet compliance norms.
Neutrality
It ensures that no organization should get punished in the name of taxes, nor should it favor any. The only purpose of taxes should be to raise revenue.
Simplicity
It ensures that tax rules should be made to be easily understandable by the taxpayers and comply with them.
Stability
It ensures that the government does not imply temporary tax rules to keep the tax codes stable and consistent throughout the financial year.
Efficiency
It ensures that the taxpayers do not face any hindrance while filing for tax and make their tax filing efficient.
Difference Between Tax Accounting and Financial Accounting
It is the ‘purpose’ that differentiates tax accounting from financial accounting.
- Tax accounting professionals calculate the figures required for paying the tax at the end of the financial year. Financial accounting aims to generate reports regarding performance and profitability.
- It is done only to calculate the taxes. Financial accounting is done to maintain the financial transaction done by a company in a quarter or year.
- It revolves around the idea of tax filing, tax planning, and government rules regarding taxes. Financial accounting is concerned with preparing financial statements like balance sheets, cash flow statements, profit and loss statements, etc.
Basics of Tax Accounting
Income tax accounting aims to calculate taxable profit and tax liability by adjusting the book profit calculated according to accounting rules. These financial statements are stored for tax audits and included in the tax return with all these workings and changes.
Deferred Tax asset
These are the items that are used to reduce taxes. For example, if your company has overpaid or paid taxes in advance, it may anticipate recovering that money. Each nation has different tax laws that apply to specific items according to GAAP. As a result of this variance, deferred tax assets and deferred tax liability are created.
Deferred Tax liability
The amount of income tax will be due in subsequent tax years concerning temporary taxable differences.
An example of a temporary difference may include the profits or revenues recognized as taxable before or after recording them into financial statements.
VAT Accounting
VAT is assessed on the gross profit at every stage of a product’s production, distribution, and sale.
Transfer Pricing
It is beneficial for tax purposes and saves taxes as a result. Transfer pricing ensures that transactions between related businesses occur at the same price as if they were between unrelated ones.
Categorization of Income
Accounting calculates the profit by taking into account all revenues and payments. The tax rate varies based on the kind of transaction; however, not all receipts are tied to the business.
Types of Tax Accounting
Everyone is subject to tax accounting, including individuals, companies, and non-profit organizations. Even tax-exempt individuals are required to engage in tax accounting. The ability to trace money linked to people and corporations is the prime goal of tax accounting.
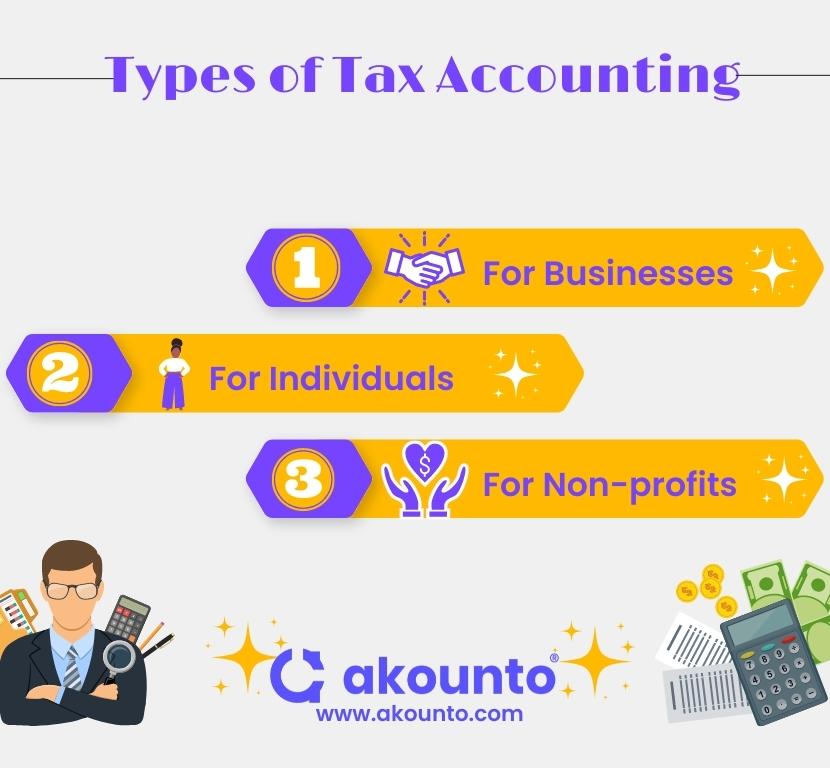
For Individuals
Tax accounting for an individual taxpayer only considers income, permissible deductions, investment profits or losses, and other activities that impact the taxpayer’s tax liability.
For Businesses
From a business perspective, additional data is required to account for taxes which includes the tax liabilities for the current year and future tax liabilities, tax credits, any refunds or penalties, earned interest, etc.
Tax accounting helps businesses in tax planning, and risk mitigation contributes to internal audits, allows adapting to the changing tax codes and procedures, etc.
For Non-Profit Organizations
The majority of tax-exempt organizations are required to submit annual returns. They must disclose all incoming funding, including donations and grants, and how the money is utilized to run the group. Even tax-exempt organizations have to file tax returns.
It ensures that all the compliances as per the law are met and that the company has reliable financial management.
Final Words
Declaring income and paying appropriate taxes is quintessential for any business from a legal and corporate governance point of view. Having accounting software that maintains accurate reports based on the data provided by the user saves time and legal hassles.
Akounto helps maintain records and generate reports, allowing businesses to make sound business decisions.




